Basics > Tables > Correlation
How correlated are the variables in the data?
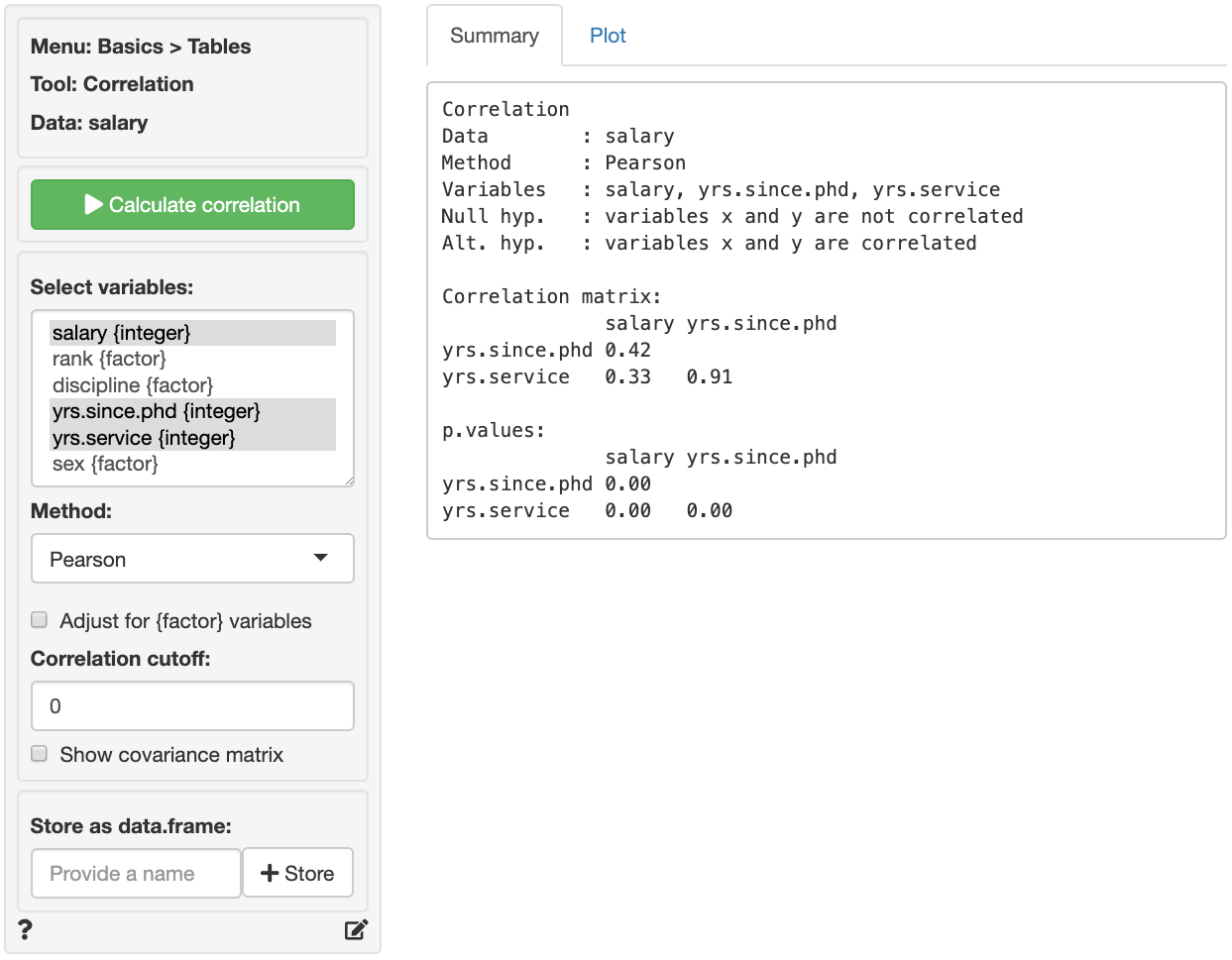
Create a correlation matrix of the selected variables. Correlations and p.values are provided for each variable pair. To show only those correlations above a certain (absolute) level, use the correlation cutoff box.
Note: Correlations can be calculated for variables of type
numeric, integer, date, and
factor. When variables of type factor are included the
Adjust for {factor} variables box should be checked. When
correlations are estimated with adjustment, variables that are of type
factor will be treated as (ordinal) categorical variables
and all other variables will be treated as continuous.
A visual representation of the correlation matrix is provided in the
Plot tab. Note that scatter plots in the graph at most 1,000
data points by default. To generate scatter plots that use all
observations use plot(result, n = -1) in Report >
Rmd.
Stars shown in the Plot tab are interpreted as:
- p.value between 0 and 0.001: ***
- p.value between 0.001 and 0.01: **
- p.value between 0.01 and 0.05: *
- p.value between 0.05 and 0.1: .
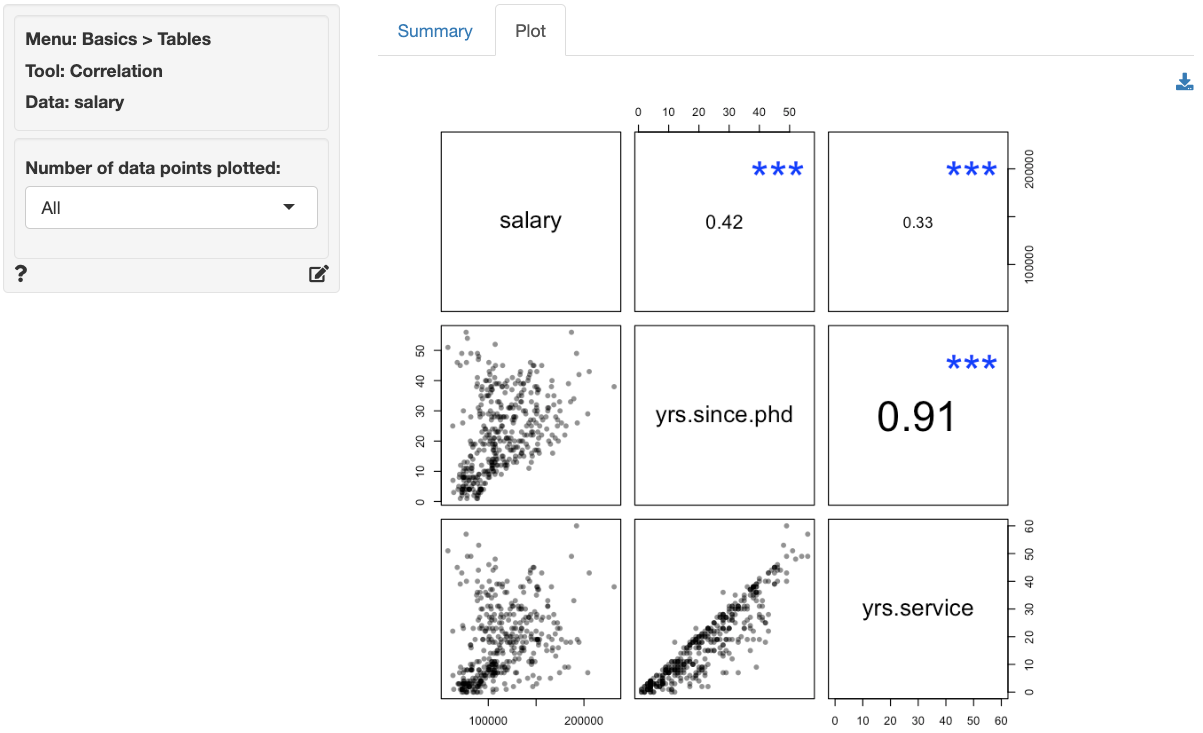
The font-size used in the plot is proportional to the size and significance of the correlation between two variables.
Method
Select the method to use to calculate correlations. The most common
method is Pearson. See
Wikipedia
for details.
Correlation cutoff
To show only correlations above a certain value choose a non-zero value in the numeric input between 0 and 1 (e.g., 0.15).
Covariance matrix
Although we generally use the correlation matrix, you can also show
the covariance matrix by checking the
Show covariance matrix box.
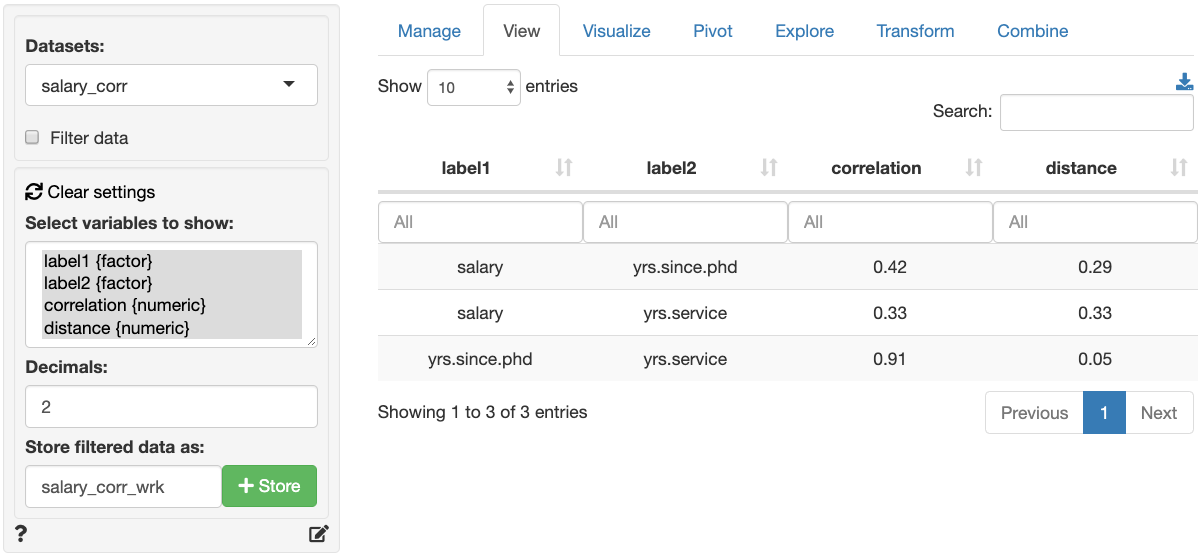
Store as data.frame
The correlation matrix can be stored as a data.frame by (1) providing
a name for the new data set and (2) clicking on the Store
button. The new data sets will the estimated correlation
for each variable pair and a distance measure that is
calculated as follows: distance = 0.5 * (1 - correlation).
This measure will be equal to 1 when the correlation between two
variable is equal to -1 and equal to 0 when the correlation between two
variables is equal to 1. For an example of what such a dataset would
look like, see the screenshot below of the Data > View tab.
Data sets with this structure can be used as input to create a
(dis)similarity based map by using Multivariate >
(Dis)similarity.
Khan on correlation
Report > Rmd
Add code to
Report
> Rmd to (re)create the analysis by clicking the
icon on the bottom
left of your screen or by pressing ALT-enter on your
keyboard.
By default the correlation plot samples 1,000 data points. To include
all data points use plot(result, n = -1) To add, for
example, a title to the plot use
title(main = "Correlation plot\n\n"). See the
R
graphics documentation for additional information.
R-functions
For an overview of related R-functions used by Radiant to evaluate correlations see Basics > Tables.
The key function from the psych package used in the
correlation tool is corr.test.